Value stream mapping can be helpful in software development engagements, as it can be used to identify and eliminate waste and improve the flow of value-adding activities in the software development process. By creating a visual representation of the steps involved in the software development process, teams can gain a better understanding of the process and identify areas where improvements can be made. This can include identifying bottlenecks, delays, and other inefficiencies in the process. Additionally, value stream mapping can be used to identify and eliminate non-value-adding activities, such as unnecessary meetings or approvals, that do not contribute to the delivery of the final product. Overall, it can be a useful tool for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of software development teams.

Some best practices when engaging in the value stream mapping process include:
- Involve cross-functional teams: Value stream mapping should involve representatives from all teams and departments involved in the process, including production, engineering, logistics, and customer service.
- Start by understanding the current state: Begin by creating a current state map of the process, which will serve as a baseline for identifying areas for improvement.
- Identify the value stream: Identify the specific product or service that is the focus of the value stream mapping process, and identify all the steps that are required to bring that product or service to the customer.
- Identify and eliminate waste: Look for activities that do not add value to the process, such as waiting, overproduction, excess inventory, unnecessary motion, and defects.
- Create a future state map: Based on the analysis of the current state map and the identification of waste, create a future state map that shows how the process could be improved.
- Implement and sustain the improvements: Based on the future state map, develop a plan for implementing the improvements and establish a system for monitoring and sustaining the improvements over time.
- Communicate the progress: Keep all stakeholders informed of the progress and benefits of the value stream mapping process.
- Continuously improve: Value stream mapping should not be a one-time event, but a continuous process of improvement, review, and adaptation.
Some of the most popular value stream mapping tools use for Agile engagements...
Kanban boards: Kanban boards are a visual tool that can be used to manage and track the flow of work through a process. They can be used to map the flow of work in an Agile software development process and identify areas for improvement.
Scrum boards: Scrum boards are similar to Kanban boards, but they are specifically designed for use with Scrum, an Agile framework for software development. Scrum boards can be used to map the flow of work in a Scrum development process and identify areas for improvement.
Value Stream Mapping Software: There are also specific software tools available for value stream mapping, like Achievion, Edraw Max, and Visio. These software tools allow teams to create and edit value stream maps, track progress, and measure improvements.
Electronic Kanban: Electronic Kanban boards like Kanbanize, LeanKit and Trello, that allow teams to manage and track work items and progress electronically. These tools can be integrated with other project management and development tools, such as Jira and GitHub.
Agile project management platforms: Some Agile project management platforms, like Jira Align, Targetprocess, and AgileCraft, also have value stream mapping functionality built in, allowing teams to map their value stream within the same tool they use to manage their Agile development process.
It's worth to mention that, these tools are not mutually exclusive, and depending on the team's needs, they could use one or several tools to achieve the best results.

The value stream mapping process should include representatives from all teams and departments that are involved in the process.
This includes, but is not limited to:
- Production: The team responsible for physically creating the product or service.
- Engineering: The team responsible for designing, developing, and testing the product or service.
- Logistics: The team responsible for managing the flow of materials, supplies, and finished products.
- Customer Service: The team responsible for communicating with customers and addressing any issues or concerns they may have.
- Quality: The team responsible for ensuring that the product or service meets the required standards of quality.
- Supply Chain: The team responsible for managing the flow of materials and supplies needed to create the product or service.
- IT: The team responsible for managing and maintaining the systems and technology that support the process.
- Management: The team responsible for overseeing the process and making decisions about how to improve it.
It's important to involve people that have knowledge of the process and have the ability to make decisions about how to improve it. It's also good to include people that are close to the process and have a good understanding of the problems and challenges that arise.
Value Stream Mapping & OKRs
Value stream mapping can be a beneficial tool when used as part of the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) development process, as it can help identify and eliminate waste and improve the flow of value-adding activities. Some specific benefits include:

Improving efficiency and productivity: By identifying and eliminating waste in the process, value stream mapping can help increase the efficiency and productivity of the process, allowing teams to achieve more with fewer resources.
Identifying areas for improvement: By creating a visual representation of the process, value stream mapping can help teams identify areas where improvements can be made, such as bottlenecks, delays, and inefficiencies.
Prioritizing objectives: By understanding the flow of value-adding activities in the process, teams can use value stream mapping to prioritize objectives and key results that will have the greatest impact on the process.
Improved communication and collaboration: Value stream mapping can help teams better understand the process, identify areas for improvement, and work together to implement changes. This can lead to improved communication and collaboration among team members.
Better alignment with customer needs: By identifying the steps required to bring a product or service to a customer, value stream mapping can help teams ensure that their efforts are aligned with customer needs and that the process is delivering value to the customer.
Better alignment with company goals: By understanding the flow of the process, teams can use value stream mapping to identify the key results that will have the greatest impact on the company's objectives and align their efforts accordingly.
Continuous improvement: Value stream mapping should not be a one-time event, but a continuous process of improvement, review, and adaptation. This will allow teams to continuously improve the process over time, and be in line with the company's goals and objectives.
9 steps to developing a solid product delivery focused value stream map.
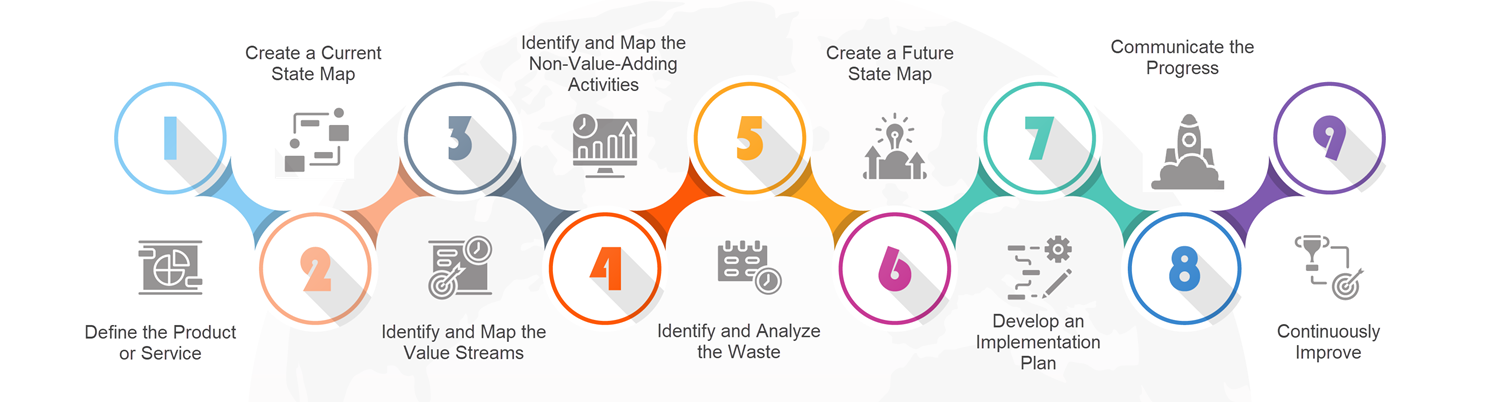
- Step 1 - Define the product or service: Identify the specific product or service that is the focus of the value stream mapping process, and clearly define its characteristics and specifications.
- Step 2 - Create a current state map: Begin by creating a visual representation of the current state of the process. This should include all the steps required to bring the product or service to the customer, including the flow of materials, information, and activities.
- Step 3 - Identify and map the value stream: Identify all the steps in the process that add value to the product or service and map the flow of value-adding activities.
- Step 4 - Identify and map the non-value-adding activities: Identify all the steps in the process that do not add value to the product or service and map the flow of non-value-adding activities.
- Step 5 - Identify and analyze the waste: Identify and analyze the types of waste present in the process, such as waiting, overproduction, excess inventory, unnecessary motion, and defects.
- Step 6 - Create a future state map: Based on the analysis of the current state map and the identification of waste, create a future state map that shows how the process could be improved.
- Step 7 - Develop an implementation plan: Based on the future state map, develop a plan for implementing the improvements. This should include timelines, resource requirements, and a system for monitoring and sustaining the improvements over time.
- Step 8 - Communicate the progress: Keep all stakeholders informed of the progress and benefits of the value stream mapping process.
- Step 9 - Continuously improve: Continuously review and improve the process over time, based on feedback, performance monitoring and changing market conditions.
It's important to mention that, this process should be collaborative and involve representatives from all teams and departments that are involved in the process, including production, engineering, logistics, customer service, and management.



Write A Comment